![Researchers say they are close to synthesizing the healthful hops compounds in the lab. [Wikipedia]](https://genengnews.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/08/Mar14_2016_Wikipedia_Hops2101941282-1.jpg)
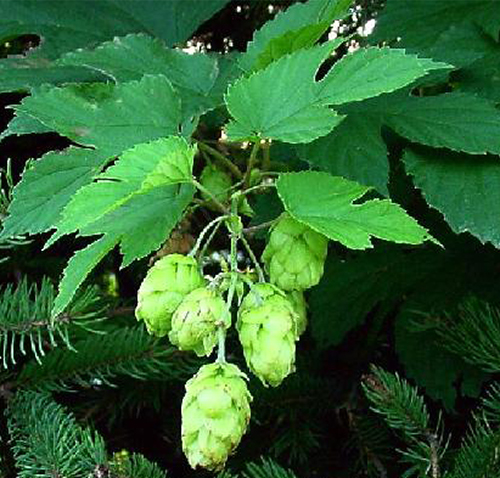
Researchers say they are close to synthesizing the healthful hops compounds in the lab. [Wikipedia]
Scientists report that they are close to synthesizing beer hop compounds in the lab. This advance could one day lead to medicines from these compounds, which have the ability to halt bacterial growth and disease, without having to extract them from plants.
The researchers discussed their work at the 251st National Meeting & Exposition of the American Chemical Society in San Diego.
“When researchers extract healthful chemicals from hops, they first have to determine whether they have separated out the specific compounds they're interested in,” says Kristopher Waynant, Ph.D., who leads the project. “But if you can figure out how to make these compounds from scratch, you know they are the right ones.”
The compounds Dr. Waynant is interested in are humulones, which are alpha acids that have anticancer and anti-inflammatory properties, and lupulones, which are beta acids that have equally important but not as well-understood biological effects. Scientists ultimately want to harness these activities potentially to improve human health. But before humulones and lupulones can be turned into effective pharmaceuticals, scientists must confirm that they are extracting the proper acids from hops. In theory, they can do this by separating the acids with high-performance liquid chromatography, but results from this method need to be compared to analytical standards, which do not yet exist for the individual compounds.
To create a library of such analytical standards, Dr. Waynant and undergraduate student Lucas Sass, both at the University of Idaho, are attempting to synthesize a set of humulones and lupulones in the lab.
The researchers start with phloroglucinol, a commercially available compound that is derived from plants. So far, they have been developing multistep processes to synthesize three types of humulones. They begin with acylation and prenylation steps, and then use transition-metal catalysis with a chiral ligand to create asymmetric products. The team is still working on tweaking the final step of converting the intermediate products in the desired humulones efficiently.
“Unfortunately, the first few pathways I proposed were not the best or most efficient,” Dr. Waynant admits. “But Lucas has gone through the literature and analyzed different ways to perform each of these steps to get the best results.”
Currently, Sass is making progress on optimizing the first two steps. “It's been a lot of trial and error,” Sass says. “But it's so exciting when an approach finally works.”
The researchers say they are getting very close to optimizing the complete method for producing humulones in the lab.
In the future, Dr. Waynant's team will continue the project to synthesize a broader range of humulones and lupulones. He also plans to reach out to and collaborate with biologists and medical researchers to develop active agents for pharmaceuticals to treat cancers or inflammatory diseases from these beer-inspired compounds.